Difference between revisions of "Herschel Space Observatory"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | The Herschels were pioneers of the systematic classification and investigation of the heavens. William Herschel was one of the first 'professional' astronomers, and discovered infrared radiation. His sister Caroline helped him to develop the modern mathematical approach to astronomy. | + | Caroline and William Herschel: The Herschels were pioneers of the systematic classification and investigation of the heavens. William Herschel was one of the first 'professional' astronomers, and discovered infrared radiation. His sister Caroline helped him to develop the modern mathematical approach to astronomy. |
William, son of a musician, was born in Hanover, Germany, in 1738. He followed in his father's footsteps, joining the Hanoverian Guard band to play the oboe, but moved to England to teach music in 1755, eventually settling in Bath in 1766. | William, son of a musician, was born in Hanover, Germany, in 1738. He followed in his father's footsteps, joining the Hanoverian Guard band to play the oboe, but moved to England to teach music in 1755, eventually settling in Bath in 1766. | ||
Revision as of 20:01, 17 January 2013
Caroline and William Herschel: The Herschels were pioneers of the systematic classification and investigation of the heavens. William Herschel was one of the first 'professional' astronomers, and discovered infrared radiation. His sister Caroline helped him to develop the modern mathematical approach to astronomy.
William, son of a musician, was born in Hanover, Germany, in 1738. He followed in his father's footsteps, joining the Hanoverian Guard band to play the oboe, but moved to England to teach music in 1755, eventually settling in Bath in 1766.
He became interested in astronomy, and started to build his own telescopes. He developed and refined Isaac Newton‘s designs to avoid problems with poor glass optics. Herschel cast and polished his own mirrors, producing ever bigger and better telescopes.
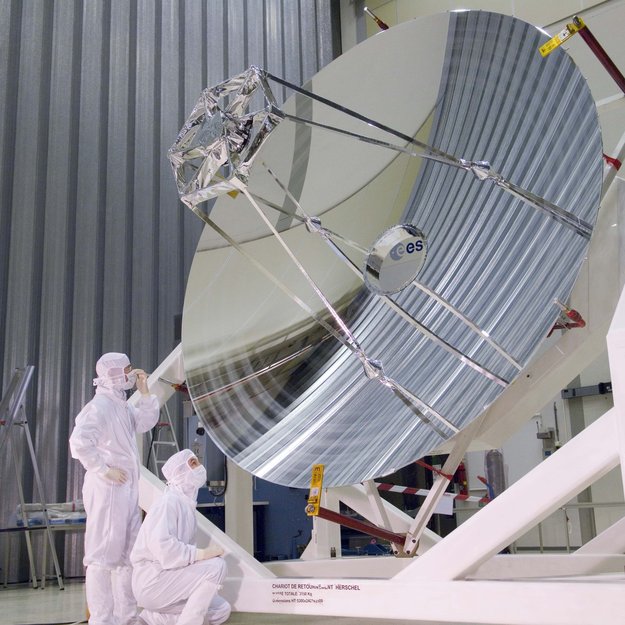
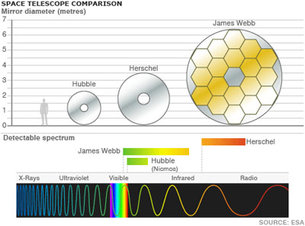
Herschel is the largest infrared space telescope ever launched. With its 3.5-m primary mirror, it is four times bigger than any previous infrared space telescope and almost one and a half times larger than the Hubble Space Telescope.
Herschel's primary mirror is the telescope's light collector. It captures the light from astronomical objects and directs it towards the smaller secondary mirror. The two mirrors work together focusing the light and directing it to the instruments, where the light is detected and analysed, and the results recorded by the onboard computer.
The size of the primary mirror is the key to a telescope's sensitivity: the bigger it is, the more light it collects, and the fainter the objects it sees. It also determines the telescope's ability to distinguish fine details. The surface of the mirror is very important, too. It has to be precisely shaped and perfectly smooth, since the slightest roughness distorts the final image.
The mirror must be light and sturdy to withstand the extreme conditions of launch (when it will be shaken with a force several times that of Earth’s gravity), and the low temperatures of outer space; and any bump on its surface must be less than a thousandth of a millimetre high. Herschel spacecraft
This technological marvel has been constructed almost entirely of silicon carbide. The primary mirror has been made out of 12 segments brazed together to form a monolithic mirror which was machined and polished to the required thickness (about 3 mm), shape, and surface accuracy.
Vital Stats:
The Herschel satellite is a tall cylinder, about 7.5 m high and 4.0 m wide, with a launch mass of around 3.4 tonnes.
| Dimensions | ~ 7.5 x 4.0 m (height x width) |
| Mass | 3.4 tonnes at launch |
| Telescope mass | 315 kg |
| Spacecraft | 3-axis stabilised |
| Telescope size | 3.5 m diameter primary mirror |
| Science data rate | 130 kbps |
| Lifetime | 3.5 years |
| Operational orbit | Lissajous orbit at an average distance of 800 000 km from L2 |
| Attitude thrusters | 12 thrusters, 20 N each |
| Solar arrays | Flat, fixed panels of triple-junction,Ga As cells, |
| Solar array area: | about 12 m2 |
| Batteries | 39 Ah Lithium ion batteries |
| Communication | 2 low gain antennae,1 medium gain antenna |