| Characteristics
|
Pros
|
Cons
|
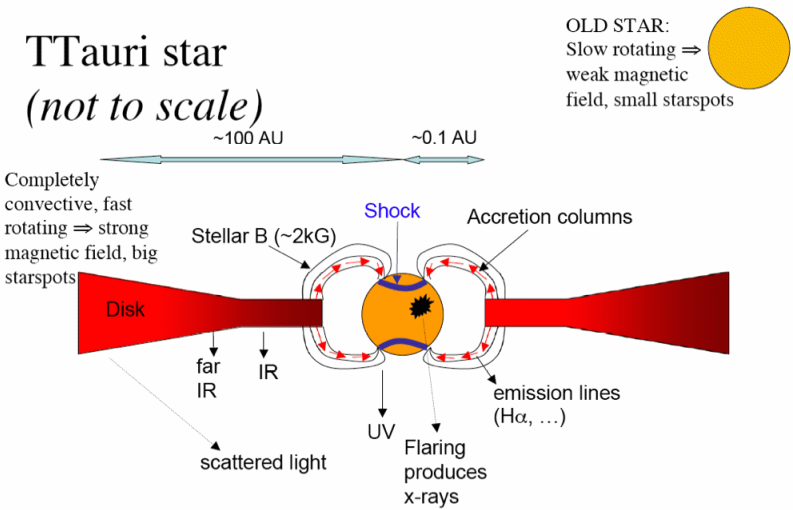
| IR Excess
(IR is emitted by circumstellar matter)
|
- Need a large field of view to efficiently study large parts of the sky at once
- need Spitzer for mid- and far-IR work (in terms of wavelength coverage and efficiently covering large parts of the sky)
- we have the data already! (this is a BIG pro!!)
- Can find all of the stars with an infrared excess pretty straightforwardly.
- Real life examples of people using this method as a primary method for finding young stars: Padgett et al., “An Aggregate of Young Stellar Disks in Lynds 1228 South,” 2004, ApJS, 154, 433; Joergensen et al., “The Spitzer c2d Survey of Large, Nearby, Interstellar Clouds. III. Perseus Observed with IRAC,” 2006, ApJ, 645, 1246
|
- need Spitzer (that is, if we didn’t already have the data, as it would be in the general case of cluster membership in general, not specifically in IC2118)
- will only find those stars which still have enough disk left to make an IR excess – will be unable to distinguish young stars without disks (Class IIIs) from the interlopers.
|
| (Flaring) X-rays
(young stars emit lots of X-rays because they are completely convective and fast-rotating, so they have lots of starspots and therefore lots of flares, big and small)
|
- Need something that can detect X-rays – CXO (Chandra X-ray Observatory) or XMM (X-Ray Multi-mirror Mission)
- Can find all of the stars that are bright in X-rays pretty straightforwardly
- Real life examples of people using this method as a primary method for finding young stars: Wolk et al., “X-Ray and Infrared Point Source Identification and Characteristics in the Embedded, Massive Star-Forming Region RCW 38,” 2006, AJ, 132, 1100, Alcala et al., “New weak-line T Tauri stars in Orion from the ROSAT all-sky survey,” 1996, A&AS, 119, 7; [note that both of these folks went out and got additional data on at least some of their objects to prove that they were members.]
|
- need space-based mission to see X-rays
- Need a large field of view to efficiently study large parts of the sky at once; all missions have small FOV (due to methodology for detection)
- takes long time (like 25,000 seconds for one 5x5 arcminute field)
- not all might be detectable
- might not be flaring
- will only find those stars that are X-ray active enough (might miss those that are deeply embedded or have big enough thick disks to block out the X-rays)
|
| Outflows
(only present for the very youngest objects, Class Os and Is)
|
- Again, need to cover large areas (outflows can extend over many parsecs).
- Easily detectable in IRAC or optical emission line studies from the ground (search in ADS on “John Bally” to find lots such optical surveys)
- Signpost to star formation – really big, obvious literal pointer saying “there is a very young star right HERE”
- Real life examples of people using this method as a primary method for finding young stars: Walawender et al., “Multiple Outflows and Protostars near IC348 and the Flying Ghost Nebula,” 2006, AJ, 132, 467, Bally et al., “Irradiated and Bent Jets in the Orion Nebula,” 2006, AJ, 131, 473
|
- orientation might not be good – if it’s pointing right at us, we’ll miss it.
- not all stars have jets
- sometimes hard to connect the maze of jets back to their source [2 main reasons: (a) central object often very embedded, and may be missed in optical and/or shallow surveys; (b) object precesses and moves, so jets twist and turn and don’t always point straight back to their source. In complicated regions (e.g., NGC 1333, see Spitzer image in press release archive), this is particularly tough.]
|
| Emission lines and other line shapes
(emitted/absorbed by accreting matter and technically disks too, though I wasn’t thinking of that at the time)
|
- Photometry: Often easy to cover large areas with ground-based telescopes and an Halpha filter.
- Spectroscopy: fast enough sequence of Halpha spectra can literally allow you to see blobs of matter as they fall into the star (!), which is pretty incontrovertible evidence you have a young star.
- If you have a single spectroscopic observation of something with a P Cygni profile, this can also indicate accretion (emission line slightly redshifted from absorption line because matter is falling into the star).
- Spectroscopy of the disk: need IR spectroscopy to see emission lines from molecules in disk
- Real life examples of people using this method as a primary method for finding young stars: Ogura et al., “Halpha Emission Stars and Herbig-Haro Objects in the Vicinity of Bright-Rimmed Clouds,” 2002, AJ, 123, 2597, Edwards et al., “Probing T Tauri Accretion and Outflow with 1 Micron Spectroscopy,” 2006, ApJ, 646, 319 [ok, this is not blind searching, but it is really using line shapes to learn more about the stars in question.]
|
- For a more precise measurement of Halpha, need to take spectra, which take longer to acquire than photometry.
- Nebula itself can emit in Halpha (especially true in Orion Nebula, M41/42), so it can be hard to distinguish the young star emission from the nebular emission (photom or spec).
- Older stars which are simply chromospherically active can emit in Halpha, so it can be hard to distinguish young stars from older stars on Halpha alone.
- Spectroscopy of the disk – usually too expensive in terms of observing time to just go hunting blindly – usually need to have some reason to suspect a star is already young before embarking on such a project.
|
| Variability
(because so much is happening in and around young stars, they are highly variable. In all cases here, I’m thinking of photometry, but as mentioned above, temporal studies using spectroscopy are also possible.)
|
- Most frequently done in V, I, and/or J bands; variability in young stars has been seen in nearly all possible wavelengths
- can do from the ground, so can cover large areas of sky if you have a large FOV camera
- with a large FOV, can do many stars at once.
- young stars highly variable, so relatively easy to do (need ~week or two rather than ~month or two of telescope time, and need only to go to 0.1 mag accuracy, not 0.001 mag accuracy, though that would help)
- can do relative photometry (photometry with respect to the other stars in the frame rather than with respect to photometric standards) so don’t really need calibrators, and you can keep observing if the night is strictly not photometric conditions.
- can be done (often best done) using small (<1 m) telescopes
- can look for periods at the same time (see below)
- Real life examples of people using this method as a primary method for finding young stars: Carpenter et al., “Near-Infrared Photometric Variability of Stars toward the Orion A Molecular Cloud,” 2001, AJ, 121, 3160
|
- takes time, need many observations per night over many nights
- need to see photosphere (or close to it), so deeply embedded stars are harder to do, or at least harder to make the case to our colleagues that we’re not seeing variation in the nebula or outer disk
- need to do both short and long integrations to be able to get valid data on the bright and faint stars, respectively.
- Older stars can vary too, but generally not at the rate or amplitude
|
| Rotation rate
(a special case of ‘variability’ above)
|
- Young stars rotate in general much faster than old stars, so fast rotation is also generally taken as evidence for youth.
- Spectroscopy: only need one observation per star.
- Spectroscopy: high-res spectra can often also tell you if there is a nearby companion
- Spectroscopy: high-res spectra can also tell you if the star still has lithum (Li burns so easily that only the youngest stars are thought to have any left)
- Photometry: know the true value (number is either really right, or wrong by a lot, as a result of observing method), no inclination (sin i) uncertainty
- Photometry: Period is often something we know with more precision than anything else about these young stars.
- Photometry: can use the same data you’re using for variability study above.
- Real life examples of people using this method as a primary method for finding young stars: Rebull, “Rotation of Young Low-Mass Stars in the Orion Nebula Cluster Flanking Fields,” 2001, AJ, 121, 1676; Makidon et al., “Periodic Variability of Pre-Main Sequence Stars in the NGC 2264 OB Association,” 2004, AJ, 127, 2228
|
- Spectroscopy: need high spectral resolution to get measurement of projected rotational velocity (v sin i)
- Spectroscopy: can’t do anything about that inclination (sin i) uncertainty
- Photometry: need many observations per night over many nights, and even then maybe only about 1% of your observed stars will be periodic.
- Photometry; need stars to cooperate -- another observing campaign on the same stars a year later will only recover about half(!) of the periodic stars, presumably due to changes in the stars themselves (star spot shape and coverage, disk ‘puffiness’, etc)
- Photometry: possible – though unlikely for fast rotation rates – to be fooled by binaries or disk occultations
|